Enhancing Soil Strength and Stability through Soil Mixing Techniques: A Focus on Deep Soil Mixing (DSM)
Soil Mixing is a ground improvement technique that reinforces the soil by mixing in situ a network of grout and soil columns.
Soil Mixing Technique
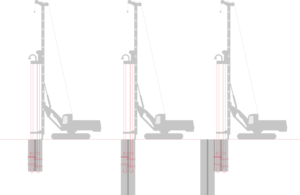
Soil mixing consists of using specially designed augers or special tools to mechanically mix the soil with an in situ binder. The process simultaneously breaks up the soil without removing it, injects a binder at low pressure and thoroughly mixes the binder with the soil.
Soil Mixing Implementation
The machine is fitted with single or multiple soil mixing tools (auger, blades, rotary head) to directly inject binder into the mixing zones. The stabilization agent is combined with the soil to be treated and robustly mixed by the mixing blades. These parameters are adopted accordingly as a function of soil strength and specifications to be achieved.
Soil Mixing Advantages
This technique is used to reduce settlement under structures, increase the load-bearing capacity of the soil, ensure stability (including reduced liquefaction), reduce thrust behind retaining structures, block ground water, increase lateral reaction around foundation piles, etc. The soil mixing technique can be used to create a wide variety of treatment geometries (isolated elements, grids, walls, cells, blocks) and can therefore be easily adapted to a wide range of structures and applications.
Soil Mixing FAQs
A wide variety of tools is available to choose from, depending on the application. For this type of application, you could for example use cutting tools to rapidly build wall or cell systems.